
UART Setup
UART (USART) is a hardware communication protocol that facilitates asynchronous serial communication between devices. It's widely used due to its simplicity and minimal hardware requirements. The article highlights two primary scenarios:
- Computer to Microcontroller Communication: This setup requires a USB-to-UART bridge, such as the CP2102 USB to TTL converter. The USB end connects to the computer, while the UART pins (TX, RX, GND) interface with the microcontroller.
- Microcontroller to Microcontroller Communication: In this case, no USB bridge is necessary. A direct connection using three wires—TX, RX, and GND—suffices. It's crucial to connect the TX of one device to the RX of the other and vice versa, ensuring proper data transmission.
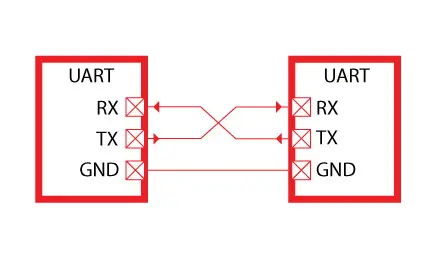 Source: microcontrollerslab.com
Source: microcontrollerslab.com
On the software side, the article suggests using serial terminal programs like RealTerm to monitor and send data over UART. These tools are invaluable for debugging and real-time communication analysis.
This function sets up UART2 with a baud rate of 9600. It calculates the USARTDIV value based on the peripheral clock (f_apb1) and configures the necessary registers to enable UART transmission and reception. Such low-level configurations are typical in embedded systems programming, offering precise control over hardware peripherals.
#define BAUD 9600
void UART2_Init(){
float usartdiv=f_apb1/(16.0*BAUD);
uint16_t mantissa=floor(usartdiv);
uint8_t uart_frac=round(16*(usartdiv-mantissa));
RCC->APB1ENR|=RCC_APB1ENR_USART2EN;
GPIOA->CRL&=~(0b11<<GPIO_CRL_CNF2_Pos);
GPIOA->CRL|=(0b11<<GPIO_CRL_MODE2_Pos)|(0b10<<GPIO_CRL_CNF2_Pos);
USART2->CR1|=USART_CR1_UE_Msk|USART_CR1_RE;
USART2->CR1&=~USART_CR1_M;
USART2->CR2&=~USART_CR2_STOP;
USART2->BRR=((uint8_t)mantissa<<4)|(uint8_t)uart_frac;
USART2->CR1|=USART_CR1_TE;
}
If you want to use DMA for UART communication, you need to initialize DMA channel for receiving, and transmitting.
From the table below you can see that UART2 RX is assigned to Channel 6 and UART2 TX to Channel 7. Therefore, you must enable and initialize those two channels.

DMA Setup
void DMA_UART2_RX_Init(void){
RCC->AHBENR|=RCC_AHBENR_DMA1EN_Msk;
DMA1_Channel6->CPAR=&(USART3->DR);
DMA1_Channel6->CMAR=&UART_RX_Data[0];
DMA1_Channel6->CCR|=0b11<<DMA_CCR_PL_Pos; //Priority very high
DMA1_Channel6->CCR&=~(0b11<<DMA_CCR_MSIZE_Pos); //8bit size
DMA1_Channel6->CCR&=~(0b11<<DMA_CCR_PSIZE_Pos); //8bit size
DMA1_Channel6->CCR&=~DMA_CCR_DIR; //Read from peripheral
DMA1_Channel6->CCR|=DMA_CCR_MINC;
DMA1_Channel6->CCR&=~DMA_CCR_PINC;
DMA1_Channel6->CNDTR=UART2_RX_CNT;
DMA1_Channel6->CCR|=DMA_CCR_TCIE; //Enable Transfer complete interrupt
NVIC_SetPriority (DMA1_Channel6_IRQn, 1); // Set Priority
NVIC_EnableIRQ (DMA1_Channel6_IRQn); // Enable Interrupt
}
void DMA_UART2_TX_Init(void){
RCC->AHBENR|=RCC_AHBENR_DMA1EN_Msk;
DMA1_Channel7->CPAR=&(USART3->DR);
DMA1_Channel7->CMAR=&UART_TX_Data[0];
DMA1_Channel7->CCR|=0b11<<DMA_CCR_PL_Pos; //Priority very high
DMA1_Channel7->CCR&=~(0b11<<DMA_CCR_MSIZE_Pos); //8bit size
DMA1_Channel7->CCR&=~(0b11<<DMA_CCR_PSIZE_Pos); //8bit size
DMA1_Channel7->CCR|=DMA_CCR_DIR; //Send to peripheral
DMA1_Channel7->CCR|=DMA_CCR_MINC;
DMA1_Channel7->CCR&=~DMA_CCR_PINC;
DMA1_Channel7->CNDTR=UART2_TX_CNT;
DMA1_Channel7->CCR|=DMA_CCR_TCIE; //Enable Transfer complete interrupt
NVIC_SetPriority (DMA1_Channel7_IRQn, 1); // Set Priority
NVIC_EnableIRQ (DMA1_Channel7_IRQn); // Enable Interrupt
}
To send data via DMA you only need to fill the DMA buffer (UART_TX_Data[]) and start DMA transfer:
void UART_DMA_TX(void){
DMA1_Channel7->CCR&=~DMA_CCR_EN; //Disable DMA channel, if not already
DMA1_Channel7->CNDTR=UART2_TX_CNT; //Set number of transactions
DMA1_Channel7->CCR|=DMA_CCR_EN; //Enable DMA channel
}
To read data via DMA you only need to start DMA transfer and read the UART_RX_Data[] array:
void UART_DMA_RX(void){
DMA1_Channel6->CCR&=~DMA_CCR_EN; //Disable DMA channel, if not already
DMA1_Channel6->CNDTR=UART2_TX_CNT; //Set number of transactions
DMA1_Channel6->CCR|=DMA_CCR_EN; //Enable DMA channel
}
void DMA1_Channel7_IRQHandler(void){
//Do stuff
}
void DMA1_Channel6_IRQHandler(void){
//Do stuff
}
Copyright 2024-2025, Mario Matovina
Send me an e-mail